props (propeties)
: 부모 컴포넌트가 자식 컴포넌트에 전달한 값
- 부모 컴포넌트 👉 자식 컴포넌트만 가능
- 부모 컴포넌트에서 호출한 자식 컴포넌트에게 props를 부여하면,
props는 객체로 묶여서 자식 컴포넌트의 매개변수로 들어간다.
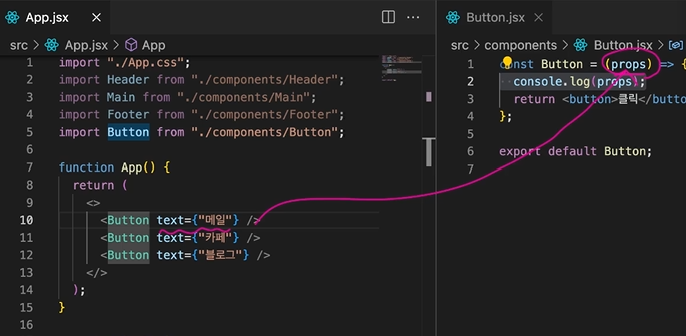
props를 통해 값에 따라 다른 UI를 보여줄 수 있다.

case 1.
1. 컴포넌트의 매개변수로 props 전달2. {props.key}로 사용
// App.jsx
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button text={"메일"} color={"red"}></Button>
<Button text={"카페"}></Button>
<Button text={"블로그"}></Button>
</>
)
}
// Button.jsx
const Button = (props) => {
return (
<button style={{color: props.color}}>
{ props.text }
</button>
)
};
export default Button;
case 2.
1. 데이터를 객체{}로 묶고
2. Spread 연산자(...) 이용해서 객체를 각각 props로 전달
3. 구조분해할당 {key명}으로 사용하기
// App.jsx
function App() {
const buttonProps = { // 1
text: "메일",
color: "red",
a:1,
b:2
}
return (
<>
<Button {...buttonProps}></Button> // 2
<Button text={"카페"}></Button>
<Button text={"블로그"}></Button>
</>
)
}
// Button.jsx
const Button = ({text, color}) => {
return (
<button style={{color: color}}>
{ text }
</button>
)
};
props는 HTML요소, React 컴포넌트도 전달할 수 있다.
1. 컴포넌트의 닫는 태그(</컴포넌트명>) 만들기
2. 컴포넌트 태그 사이에 HTML 요소 / React 컴포넌트 넣기
3. 컴포넌트의 매개변수로 children 추가하기
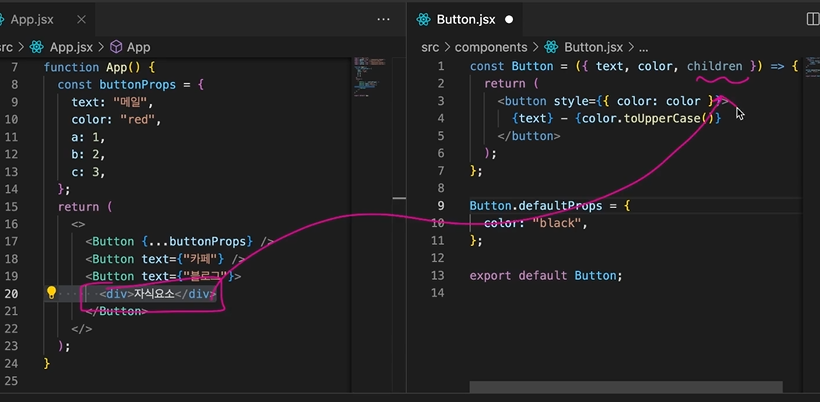
// App.jsx
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button text={"메일"} color={"red"}/>
<Button text={"카페"}/>
<Button text={"블로그"}>
<div>자식요소</div>
<Header/>
</Button>
</>
)
}
// Button.jsx
const Button = ({text, color, children}) => {
return (
<button style={{color: color}}>
{ text }
{ children }
</button>
)
};
props 기본값 설정하기
컴포넌트명.defaultProps { 기본값 설정 }
Button.defaultProps = {
color: "black"
};
출처
한입 크기로 잘라먹는 리액트