✅ 컴포넌트 종류
- Stateless Component
(Presebtational Component)
: 표현 목적의 컴포넌트(마크업, 스타일링)
- Stateful Component
(Container Component)
: 상태가 있는(변경되는) 컴포넌트
✅ 리액트가 다루는 데이터 타입
1. 컴포넌트 속성(props): 읽기 전용
- 수정 ❌
2. 컴포넌트 상태(states): 읽기 / 쓰기
- 컴포넌트 트리(렌더 트리 A)➡️ 화면 렌더링
- 컴포넌트 트리(렌더 트리 Z) ➡️ 화면 업데이트
- 시간의 흐름에 따라 화면 갱신(업데이트)👉 상태(state) 사용
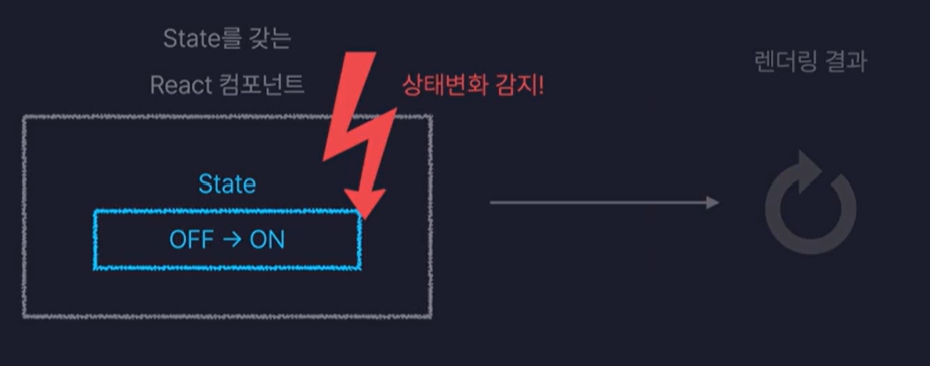
📌 State(상태)
: 컴포넌트 내부의 데이터를 기억하는 것
📌 useState
: 컴포넌트에 state 변수를 추가할 수 있는 React Hook
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState)- state: 저장한 값을 가진 state 변수
- setState: state 변수를 업데이트하고, React에 컴포넌트를 다시 렌더링하도록 유발하는 setter 함수
- useState()에 콜백 함수를 넣으면, 비용이 큰 초기값의 계산을 지연해서 성능을 최적화 할 수 있다.
- setState 함수에 콜백 함수를 넣으면, 현재 상태값을 기반으로 새로운 상태를 계산할 수 있다.
이 방식은 이전 상태값을 참조해야 할 때 유용하다. - 상태와 상태 변경 함수를 배열로 반환
- useState를 호출 👉 React에 이 컴포넌트가 무언가를 기억하기를 원한다고 말하는 것이다.
- 함수 컴포넌트에서 사용

✨ 리 렌더링(Re-Rendering)이 발생하는 상황
- 자신의 state값이 변경되면
- 부모에게 제공받은 props값이 변경되면
- 부모 컴포넌트가 리렌더링되면
- useState 훅의 업데이트 함수는 상태를 합성하지 않고 덮어쓴다.
→ 객체 또는 배열 타입의 데이터를 상태로 관리할 경우, 데이터를 직접 합쳐 주어야 함(spread syntax)
const handleUpdateFormData = (e) => {
const { name, value } = e.target;
const nextFormData = {
// formData가 없으면 content를 입력하는 순간
// title 내용이 없어져 버림
...formData,
[name]: value,
};
setFormData(nextFormData);
};
✅ useState 사용 순서
- 상태 & 상태 업데이트 정의
- 이벤트 핸들러 함수에서 상태 업데이트
- 파생된 상태
- 컴포넌트의 상태(state) 또는 속성(props)에 의해 다시 계산되는 값 - JSX 생성
1️⃣ 상태 & 상태 업데이트 정의
(1) import로 내장 함수인 useState 불러옴
import { useState } from 'react'
(2) 함수 컴포넌트 내에서 useState 선언
const [state, setState] = useState(state 초기값);- 상태 변화 함수는 setXXX으로 작명
2️⃣ 이벤트 핸들러 함수 내부에서 상태 업데이트
set업데이트 함수(수정할 state값); const handleCheck = (e) => {
const nextCheckedValue = e.target.checked;
// 선언된 리액트의 컴포넌트 상태 업데이트 트리거(렌더 요청)
setChecked(nextCheckedValue);
};
3️⃣ 파생된 상태
- 컴포넌트의 상태(state) 또는 속성(props)에 의해 다시 계산되는 값
const searchedUsersList = users.filter(
(user) => user.name.includes(searchTerm) || user.email.includes(searchTerm)
);
4️⃣ JSX 생성
- return문 안에서 호출
{ state명 }function App() {
const [state, setState] = useState(4);
return (
<>
<h1>{state}</h1>
</>
)
}
예제 1) 체크박스 컴포넌트
import './TermAndConditions.css';
import React from 'react';
function TermAndConditions() {
// 컴포넌트의 상태 선언
const [checked, setChecked] = React.useState(false);
// 이벤트 핸들러 함수(상테 업데이트 로직 포함)
const handleCheck = (e) => {
const nextCheckedValue = e.target.checked;
// 상태 업데이트 트리거(렌더 요청)
setChecked(nextCheckedValue);
};
// 파생된 상태(데이터)
// - 리액트가 렌더 트리거를 받아 렌더하면 다시 계산
const isDisabled = checked ? false : true;
return (
<form className="TermAndConditions">
<h2>이용 약관</h2>
<p>
OOO 서비스를 이용함으로써 귀하는 본 약관에 동의하게 되므로 본 약관을
숙지하는 것이 중요합니다. 본 약관 외에도 OOO은 개인정보처리방침을
게시합니다.
</p>
<div>
<input
id="terms"
name="terms"
type="checkbox"
checked={checked}
onChange={handleCheck}
/>{' '}
<label htmlFor="terms">이용 약관에 동의합니다.</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" disabled={isDisabled}>
확인
</button>
</form>
);
}
export default TermAndConditions;
예제 2) 텍스트 확장 컴포넌트
- `children` 속성(prop) 길이에 따라 확장 가능한 텍스트 렌더링
- `limit` 속성(기본 값: 255) 값보다 `children` 길이가 짧은 경우 텍스트만 표시
- `limit` 속성 값보다 `children` 길이가 긴 경우 텍스트 말줄임(...) 표시
- `limit` 속성 값보다 `children` 길이가 긴 경우 확장 or 축소 버튼 표시
- 확장 or 축소 버튼을 사용자가 클릭하면 텍스트 확장 또는 축소되어 표시
import { string, number } from 'prop-types';
import { useState } from 'react';
import './ExpandableText.css';
// 타입 검사
ExpandableText.propTypes = {
children: string.isRequired,
limit: number,
};
function ExpandableText({ children, limit = 255 }) {
// 컴포넌트 상태를 객체로 선언
const [state, setState] = useState({
// 축소되어 있는 상태(확장 false)
isExpand: false,
});
// 텍스트 길이(boolean)
const isExpandable = children.length > limit;
let renderText = children;
if (isExpandable) {
// limit보다 길이가 긴 텍스트는 limit 부터 '...' 붙이기
renderText = children.slice(0, limit) + '...';
}
// 버튼 텍스트 변경
const buttonLabel = state.isExpand ? '축소' : '확장';
console.log(state.isExpand)
// 이벤트 핸들러 함수
const handleExpand = () => {
// 확장되어 있는 상태면 true 변수 선언
const nextExpandValue = !state.isExpand;
// 컴포넌트 상태 업데이트
// - isExpand(축소되어 있는 상태)를 true(확장 true)로 변경
setState({
isExpand: nextExpandValue,
});
};
return (
<div className="ExpandableText">
<p>{state.isExpand ? children : renderText}</p>
{/* 텍스트 길이가 limit보다 크면 */}
{isExpandable && (
<button type="button" onClick={handleExpand}>
{buttonLabel}
</button>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default ExpandableText;
예제 3) 아바타 프로필 컴포넌트
- 데이터 분리
- 컴포넌트 상태로 정의(선언)
- 이벤트 핸들러 작성(기능 구현)
- 사용자 상호작용에 따라 화면 업데이트 (확인)
- 컴포넌트 테스트 (SKIP)
import { useState } from 'react';
import Avatar from '@/components/Avatar';
import { avatarsData } from '@/data/avatars';
function AvatarListPage() {
// 컴포넌트 상태 선언
const [list, setList] = useState(avatarsData);
// 삭제 이벤트 핸들링 함수(상태 업데이트 로직)
const handleDeleteItem = (deleteId) => () => {
// 삭제된 프로필을 제외한 남은 프로필(변경 후의 상태 데이터)
const nextList = list.filter((item) => item.id !== deleteId);
// - deleteId: 현재 삭제 버튼을 누른 프로필 ID
// - item.id: 데이터에 저장된 프로필 ID
// 상태 업데이트 (렌더 트리거)
setList(nextList);
};
// 프로필이 다 삭제되면
if (list.length === 0) {
return <p style={{ fontSize: 24 }}>화면에 표시할 아바타가 없습니다. 😳</p>;
}
return (
<ul className="AvatarList">
{list.map((item) => (
<li key={item.id} style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>
<Avatar name={item.name} photo={item.photo} status={item.status} />
<button
type="button"
onClick={handleDeleteItem(item.id)}
style={{ marginBlockStart: 8 }}
>
삭제
</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
export default AvatarListPage;
예제 4) 카운터 컴포넌트
- `count` 속성(prop, 기본 값: 1)을 전달받아 화면에 표시
- `step` 속성(기본 값: 1)을 전달받아 버튼 레이블에 표시
- `min` 속성(기본 값: 1) 보다 `count` 값이 크거나 같아야 함
- `max` 속성(기본 값: 1000) 보다 `count` 값이 작거나 같아야 함
- 사용자가 감소 버튼을 클릭하면 `count` 감소 (step 만큼)
- 사용자가 증가 버튼을 클릭하면 `count` 증가 (step 만큼)
- 사용자가 감소 버튼을 클릭했을 때 `count` 값이 `min` 보다 작거나 같을 경우 감소 버튼 비활성화
- 사용자가 증가 버튼을 클릭했을 때 `count` 값이 `max` 보다 크거나 같을 경우 증가 버튼 비활성화
* useState()에 콜백 함수를 넣어서 콜백 함수로 연산된 값을 state로 사용할 수 있다❗
import { useState } from 'react';
import { number } from 'prop-types';
import './Counter.css';
// 타입 검사
Counter.propTypes = {
count: number,
step: number,
min: number,
max: number,
};
function Counter({ count: initialCount = 1, step = 2, min = 1, max = 1000 }) {
// count 변수에 initialCount 변수 할당, initialCount가 없으면 1 할당(구조 분해 할당)
const [count, setCount] = useState(() => {
// useState()에 콜백 함수를 넣어서 콜백 함수로 연산된 값을 state로 사용
if (initialCount < min || initialCount > max) {
throw new Error(`count 값이 min 보다 작거나, max보다 큽니다.`);
}
return initialCount;
// return한 initialCount를 count(state) 값으로 설정함
});
const handleDecrease = () => {
const nextCount = count - step;
setCount(nextCount);
};
const handleIncrease = () => {
const nextCount = count + step;
setCount(nextCount);
};
// 버튼 비활성화 기준
// - 증가 버튼 = 현재 값 <= 최솟값
const isDisabledDecrease = count <= min;
// - 감소 버튼 = 현재 값 >= 최댓값
const isDisabledIncrease = count >= max;
return (
<div className="Counter">
<button
type="button"
disabled={isDisabledDecrease}
onClick={handleDecrease}
>
-{step}
</button>
<output>{count}</output>
<button
type="button"
disabled={isDisabledIncrease}
onClick={handleIncrease}
>
+{step}
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Counter;
<!-- Playground.jsx -->
<Counter count={3} min={2} max={6} />
class 컴포넌트
- class 컴포넌트에서는 setState()로 state를 변경해주면, class 내부의 render 함수를 따로 지정하지 않아도(인수로 넘겨주지 않아도) 렌더를 실행해준다.
- 레거시 방법이므로 참고만 하기
import { Component } from 'react';
import './TermAndConditions.css';
class TermAndConditions extends Component {
constructor(props) {
// 컴포넌트에 전달된 속성(props)는 읽기 전용
super(props);
// 컴포넌트의 데이터 기억(메모리)
// 컴포넌트 속성(props)와 달리 상태 값 수정 가능
this.state = {
agreement: false,
};
}
render() {
const { agreement } = this.state; // { agreement: boolean }
// 컴포넌트 속성 또는 상태로부터 파생된 상태 (derived state: from state or props)
const isDisabled = agreement ? false : true;
return (
<form className="TermAndConditions" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<h2>이용 약관</h2>
<p>
OOO 서비스를 이용함으로써 귀하는 본 약관에 동의하게 되므로 본 약관을
숙지하는 것이 중요합니다. 본 약관 외에도 OOO은 개인정보처리방침을
게시합니다.
</p>
<div>
<input
id="terms"
name="terms"
type="checkbox"
checked={agreement}
onChange={this.handleCheck}
/>{' '}
<label htmlFor="terms">이용 약관에 동의합니다.</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" disabled={isDisabled}>
확인
</button>
</form>
);
}
handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
};
// 사용자에 의한 액션에 의한 컴포넌트의 상태 업데이트
handleCheck = (e) => {
const { checked: nextAgreement } = e.target;
// 리액트에게 렌더 트리거(요청)
// - 클래스 컴포넌트에서의 상태 업데이트 API: this.setState(nextState)
this.setState({ agreement: nextAgreement });
};
}
export default TermAndConditions;
📢 핵심 정리
- 리액트는 "선언적"이다.
- 리액트의 컴포넌트는 내부에 데이터를 기억할 수 있다. (= "상태(state)")
- 리액트에서 다루는 데이터는 "속성(props)"과 "상태(states)"이다.
- 리액트에서 다루는 데이터 중
- 읽기/쓰기가 가능한 데이터는 "상태"이다.
- 읽기만 가능한 데이터는 "속성"이다. - 리액트에 의해 "선언된 상태"는 업데이트가 가능하다.
- 업데이트 된 선언된 상태를 감지해 리액트는 JSX를 반환하는 함수(또는 render 메서드)를 다시 실행한다.
- JSX를 반환하는 함수(또는 render 메서드)를 다시 실행되면, 이를 ReactDOM이 실제 DOM에 반영(commit)한다.
- 반영된 DOM을 브라우저는 다시 페인팅(Painting) 한다.
State: 컴포넌트의 기억 저장소 – React
The library for web and native user interfaces
ko.react.dev
useState – React
The library for web and native user interfaces
ko.react.dev