📌 명령형 프로그래밍(Imperative Programming)
: 프로세스의 세부 동작을 직접 제어하고 관리하는 방식
- 어떻게 수행해야 하는가(HOW you do something)
- 집에 가는 길을 구구절절 설명함(먼저 버스를 타고...) - 애플리케이션이 상태를 어떻게 변화시키고, UI를 어떻게 업데이트할지에 대해 직접 지시
- 웹 API + JavaScript 사용
예제) 체크박스
// 대상 찾기
const container = document.getElementById('imperative-programming');
const checkbox = container.querySelector('input[type="checkbox"]') as HTMLInputElement; // 타입 단언(Type Assertion)
const button = container.querySelector('button');
// 찾은 대상에 이벤트 연결
checkbox.addEventListener('change', handleChange);
// 이벤트 핸들러(기능) 작성(구현)
function handleChange(e) {
const { checked } = e.target;
if (checked) {
// button.setAttribute('disabled', 'false');
button.removeAttribute('disabled');
button.textContent = '활성 상태';
} else {
button.setAttribute('disabled', 'true');
button.textContent = '비활성 상태';
}
}
📌 선언적 프로그래밍(Declarative Programming)
: 결과를 선언하고 시스템에 세부 사항을 맡기는 방식
- 무엇을 수행해야 하는가(WHAT you do)
- 집에 가는 길을 네비게이션에 검색함 - 세부적인 구현 방식을 신경 쓸 필요 없이 상태와 뷰의 관계를 선언적으로 정의
- 선언적 프로그래밍을 위한 도구 사용(createState.js)
✨ 리액트는 "선언형 프로그래밍" 이다.
- 리액트: 컴포넌트 기반 구성
- 엘리먼트(트리)끼리 비교 👉 변경된 걸 인지 후 업데이트
- 변경된 걸 인지하는 기준 👉 상태(state)
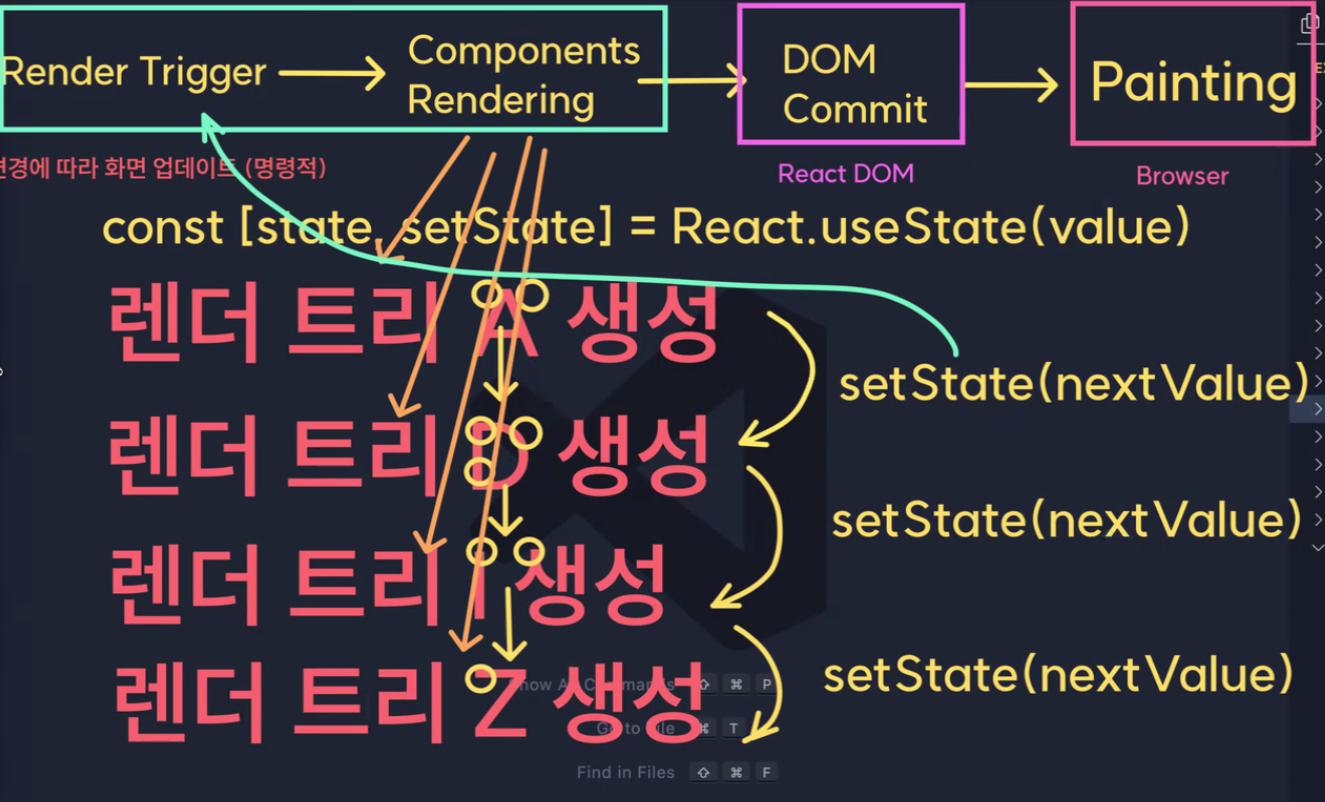
✅ 선언적 프로그래밍 순서
- 컴포넌트의 다양한 시각적 state를 확인하기
- 사용자가 볼 수 있는 UI의 모든 “state”를 시각화(버튼 활성화 UI, 비활성화 UI 등) - 무엇이 state 변화를 트리거하는지 알아내기
- 트리거 유형
(1) 휴먼 인풋: 버튼 클릭, 필드 입력, 링크 이동 등
(2) 컴퓨터 인풋: 네트워크 응답, 타임아웃, 이미지 로딩 등
- useState를 사용해서 메모리의 state를 표현하기
- 가능한 모든 시각적 state를 커버할 수 있는 확실한 것을 먼저 추가하는 방식으로 시작
- 불필요한 state 변수를 제거하기
- state가 사용자에게 유효한 UI를 보여주지 않는 경우를 방지
- state가 역설적이지 않은가
(ex. isTyping과 isSubmitting이 동시에 true일 수는 없다.) - 다른 state 변수에 이미 같은 정보가 담겨있진 않은가
(ex. isEmpty와 isTyping은 동시에 true가 될 수 없다.) - 다른 변수를 뒤집었을 때 같은 정보를 얻을 수 있진 않은가
(ex. isError는 error !== null로도 대신 확인할 수 있다.)
- state가 역설적이지 않은가
- state 설정을 위해 이벤트 핸들러를 연결하기
예제) 체크박스
import createState from "../lib/createState";
const container = document.getElementById("declarative-programming");
const checkbox = container.querySelector('input[type="checkbox"]');
const button = container.querySelector("button");
// 상태로 사용할 데이터 정의
const data = {
checked: false,
};
// 상태 선언
const [state, setState] = createState(data, render);
// 상태 업데이트가 감지되면 실행될 콜백 함수
// -> 설정된 렌더 함수 실행
// -> 컴포넌트 렌더링 프로세스 (작동, 다시 작동 ....)
// -> UI 업데이트 제어
const render = () => {
const { checked } = state;
// UI 업데이트(다시 렌더링)
(checkbox as HTMLInputElement).checked = checked;
if (checked) {
button.removeAttribute("disabled");
button.textContent = "활성 상태";
} else {
button.setAttribute("disabled", "true");
button.textContent = "비활성 상태";
}
};
const update = (globalThis.update = (value: boolean): void => {
setState("checked", value);
});
checkbox.addEventListener("change", (e: Event) => {
const { checked: nextCheckedValue } = e.target as HTMLInputElement;
// 상태 업데이트 시도
update(nextCheckedValue);
});
createState.ts
- ECMAScript
const createState = (data, callback) => {
let allowUpdate = false;
const state = new Proxy(data, {
get(target, prop) {
return target[prop];
},
set(target, prop, newValue) {
if (!allowUpdate) {
console.warn('🚫 스토어 데이터를 직접 수정할 수 없습니다.');
return false;
}
target[prop] = newValue;
callback?.();
return true;
},
});
const action = (key, value) => {
allowUpdate = true;
state[key] = value;
allowUpdate = false;
};
return [state, action];
};
export default createState;
- TypeScript
interface State {
[key: string | symbol | number]: any;
}
type StateAction = (key: string, value: any) => void;
const createState = (
data: State,
callback: () => void
): [Readonly<State>, StateAction] => {
let allowUpdate: boolean = false;
const state: State = new Proxy(data, {
get(target, prop) {
return target[prop];
},
set(target, prop, newValue) {
if (!allowUpdate) {
console.warn('🚫 스토어 데이터를 직접 수정할 수 없습니다.');
return false;
}
target[prop] = newValue;
callback?.();
return true;
},
});
const action: StateAction = (key: string, value: any) => {
allowUpdate = true;
state[key] = value;
allowUpdate = false;
};
return [state, action];
};
export default createState;
State를 사용해 Input 다루기 – React
The library for web and native user interfaces
ko.react.dev